Have you ever come across a URL that seems legitimate at first glance, yet there is something fishy about it? In most cases, if you look closely, you will notice something slightly strange about these websites, perhaps a character that doesn’t quite fit or a slight variation in the spelling. This is a classic case of homoglyphing, one of the most prevalent and insidious tactics employed by cybercriminals in their phishing.
The aim and execution of these types of attacks are simple—playing on the visual similarity between characters to create a convincing yet fraudulent version of a trusted site. This is done to deceive you into believing that you’re interacting with a familiar website. For instance, they might replace “o” (lowercase alphabet) in “google.com” with “0” (numeric zero) to create something like “g0ogle.com”, which at a cursory glance does not ring any alarms.
The thing about homoglyphs is that they are as apparent as they are elusive. That is to say, spotting them from afar is an art. And we can help you master it!
This article talks about everything you should know about homoglyphing, from its tactics to practical tips on how to defend against such deceptive attacks.
What Exactly is Homoglyphing?
A technique that capitalizes on trust and natural oversight, homoglyphing exploits the similarities between characters from different alphabets or scripts, which are likely to go unnoticed by the casual user.
For instance, can you spot the difference between a Latin lowercase ‘l’ and an uppercase ‘I’ or the number ‘1’, especially when these characters are sandwiched between other characters of the URL? Most likely not! This simple mistake serves as a lucrative opportunity for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and coax users into revealing sensitive information like passwords, bank details, etc.
Some of the common homoglyphs that you should watch out for are:
- Latin ‘a’ and Cyrillic ‘а
- Latin ‘e’ and Cyrillic ‘е’
- Latin ‘c’ and Cyrillic ‘с’
- Latin ‘p’ and Cyrillic ‘р’
- Latin ‘g’ and Script ‘g’

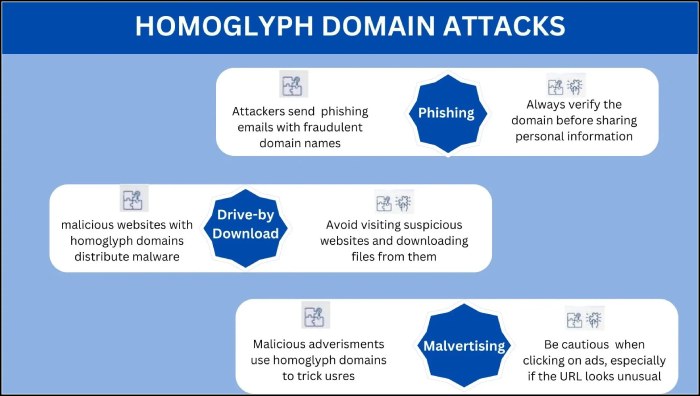
How Do Homoglyphs Lead the Way to Phishing Attacks?
One word that can be attributed to “phishing attacks” is deception, and when it comes to homoglyphs, deception reaches a whole new level of sophistication. While you might think that it would be easier to sniff homoglyphing attempts from afar, you probably never have encountered one. The disguise is often so well crafted that it fools even the most cautious individuals, leading them to fraudulent sites that mirror legitimate ones.
Let us take you through how homoglyphs facilitate phishing attacks, the archetype of deception.
Mimicking the Domain
Since a domain is the digital identity proof for any business, it is an obvious target for cyber attackers to execute their nefarious goals. By creating a fraudulent domain that has an uncanny resemblance to the legitimate domain (except for a few characters), these bad guys lay the foundation of a phishing attack. This foundation goes beyond creating a similar-looking website; it’s about crafting an entire experience that mirrors the legitimate one in every possible way, thereby leaving no room for suspicion.
Sending Fraudulent Emails
Once the foundation stone is laid, that is, the fraudulent domain is fully established, and the attackers then move to the next critical phase of their phishing strategy: sending fraudulent emails. Just like the deceptive domains, these emails are crafted with utmost attention to make them highly convincing. Their strategy involves sending out emails from the homoglyph domain to create credibility and establish trust.

Imagine receiving an email from “support@y0urbank.com”, instead of “support@yourbank.com”, informing you about a transaction you never made. The sense of urgency and the realistic look of the email can easily catch you off guard and lure you into engaging with it.
This is how you might end up as a victim of a sophisticated phishing attack.
What are the Protective Measures that You Should Follow?
Protecting your organization against homoglyphing isn’t just about avoiding a small slip-up; it’s about avoiding more severe consequences, such as financial loss, loss of critical data, reputational damage, and more.
Here are a few strategies to protect yourself from homoglyph phishing attacks:
- Properly scrutinize the URLs to look out for any red flags before clicking them
- Implement email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, to verify the source of your incoming emails
- Implement browser security solutions
- Stay up-to-date with the latest threats and trends in the cybersecurity industry
It is important to understand that avoiding homoglyph attacks not only requires vigilance but also a commitment to maintaining updated security measures and implementing robust security measures. But where do you start?
Deploying email authentication protocols like Sender Policy Framework (SPF) is undeniably a trusted approach when it comes to ensuring comprehensive email security. This protocol helps you confirm the legitimacy of the incoming emails by checking the sending server’s IP address against a list of authorized IP addresses for the domain.
Want to know more about how SPF can be your ally in bolstering email security? Get in touch with us today!

