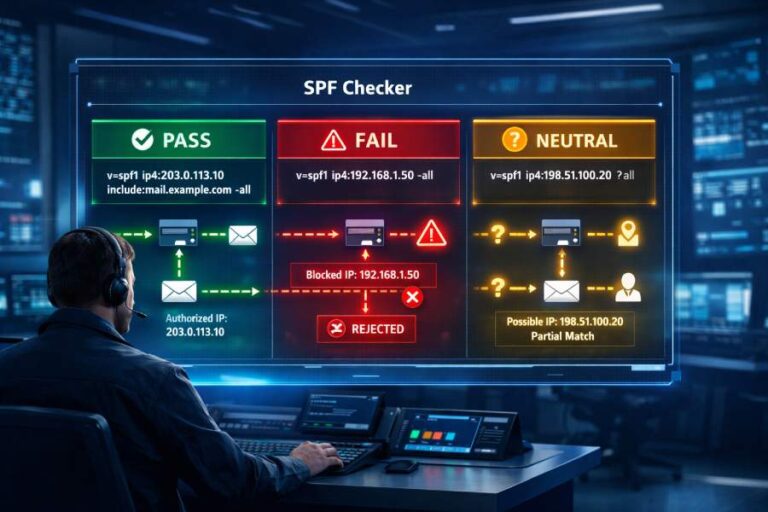
Implementing SPF is basically listing all the addresses and sources that send email on your behalf. But that’s only a surface-level understanding of the protocol. In reality, SPF works on a much deeper level. It lets the receiving server check if the incoming email is really coming from where it claims to. We say this because sometimes attackers use your domain to send fraudulent emails to your recipients that appear to come directly from you. SPF flags such emails by verifying whether the sender is actually authorized to use your domain.
But as with any other security protocol, if it is not configured properly, anyone can be let into your recipients’ mailboxes, even if they are a malicious threat actor pretending to be you. This means that when SPF isn’t set up or aligned correctly, the system can’t always tell the difference between what’s real and what’s not. That means fake emails might slip through, while genuine ones end up in spam or never reach your recipients at all.
In this article, we will understand what the main reasons for SPF misalignment are and what happens when the email authentication protocol isn’t configured properly.

Why is SPF an important part of your email security strategy?
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is considered the foundation of any email authentication strategy. It is essentially the first line of defense that prevents attackers from entering your clients’ mailboxes. Because once a spoofed email lands there, the damage is already done.
Now, let’s understand why we say that SPF is the foundation of any email security setup that you cannot afford to get wrong:
It keeps unauthorized servers away
SPF basically makes sure that only the servers you’ve approved can send emails using your domain name. When someone receives an email from you, their mail server checks where it came from and compares it with the list of allowed senders in your SPF record.
If the sender is listed on the SPF record, it lets the email in, but if it is not on the list, it doesn’t pass the check, and either goes to spam or gets blocked altogether.

It protects your customers from phishing attacks
When attackers send out fraudulent emails pretending to come from you, they usually aim to dupe your customers into divulging their personal information, clicking on malicious links, or even making payments to the wrong account. SPF helps stop that before it happens. It does so by checking whether an email is actually sent from your approved servers. It prevents those fake messages from reaching your customers in the first place.
It improves email deliverability
SPF does more than just stop spoofed or fraudulent emails from entering your clients’ mailboxes; it also ensures that legitimate emails reach their intended recipients. When your SPF record is set up correctly, it signals to receiving mail servers that your domain is trustworthy and well-managed.
That means your messages are less likely to be marked as spam or rejected, and your domain’s sender reputation will gradually improve.
What happens when SPF isn’t configured properly for your domain?
Clearly, SPF is the foundation of your email security setup, but that’s only until it is set up properly. If you somehow get it wrong, even slightly, the whole system can start working against you. So, instead of protecting your brand, a misconfigured SPF record can end up damaging it.
Here’s all that can go wrong if you don’t implement SPF properly:
Legitimate emails start failing authentication
All your email authentication and security efforts will go in vain if your legitimate emails start failing the very checks meant to protect them. This usually happens when one of your genuine sending sources, such as the CRM platform or the marketing tool that you use, isn’t listed in your SPF record.

If the sender isn’t on your approved list, the receiving mail server won’t trust the email. It will think the message might be fake and either move it to spam or block it completely.
Fraudulent emails might slip through the cracks
When SPF isn’t configured the right way, it can leave gaps that attackers can easily exploit. They can send fake emails that look like they come from you, with the complete name, similar brand narrative style, and visual identity.
Since your SPF record isn’t properly verifying who’s allowed to send emails for your domain, the receiving servers may not catch these fakes. That means those fraudulent messages can reach your customers’ inboxes without raising any red flags.

Your domain reputation takes a hit
Every time your email fails to reach its destination or spoofed messages go out in your name, it affects how mail servers see your domain. These systems track your sending behavior over time, and repeated SPF failures or impersonation attempts lower your sender reputation.
Once that reputation drops, even your genuine emails start facing deliverability issues, which, we assume, is the last thing you want for your brand.
Is SPF configuration really complicated?
It is not complicated, but it is definitely filled with technical nuances. On the surface, creating an SPF record is simple; you just define which mail servers are allowed to send emails for your domain. But the tricky part lies in the details: making sure you include all your legitimate senders, avoiding syntax errors, and staying within the DNS lookup limit. Even the slightest of mistakes, like an extra space or a typo, can trigger SPF failures.

It is safe to say that SPF configuration isn’t hard, but it is unforgiving if you don’t get it right! So, to avoid such failures and unnecessary email disruptions, it is important that you implement it with utmost attention to detail. Or even better, trust someone who knows the process inside out.
If you need help implementing SPF for your domain, our team is here to take the load off your shoulders. To know how, get in touch with us today!